Sat
24
May
2014
Maltese woman 5,600 years ago
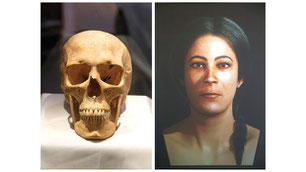
The fact that most of the neolithic sculptures found in Malta are clearly female, led to the assumption that women had a very important role in society.
During the final phase of the Neolithic period, 22 major temples were built on Malta and another 6 temples on Gozo. The temple period lasted from about 3800 BC to 2500 BC, ie about 1,000 years. The temples were built by a people, who presumably reached the islands from Sicily from the archipelago about 8,000 to 6,000 years ago.
Wed
22
Jan
2014
Venus of Willendorf

The Venus of Willendorf is a Venusfigurine from the Upper Palaeolithic, the Gravettian, and can be seen as Austria's most famous treasure piece today at the Natural History Museum in Vienna.
The representation is so realistic that an invention is considered as excluded. Some rests of paint that remain show, that the sculpture was originally covered with red ocher.
So-called "venus figurines",
female nudes standing upright, designed to be stuck in the ground, and then covered with red ochre, were made as an unbroken artistic and symbolic tradition of the Eurasian continent that lastet
for at least 30.000 years (between 40.000 B.C-10.000 B.C).
Sun
02
Jun
2013
Thera - Atlantis

What kind of role women had on ancient Thera cannot be said with certainty, since the scripture (Linear A) has not been deciphered, everybody may interpret the images for themselves. Nevertheless the leading role of the illustrated women is undeniable.
There is some archaeological, seismological, and vulcanological evidence that the myth of Atlantis, described by Plato (Kritias und Timaios) is Thera.
In 1700 or 1600 BCE the probably biggest vulcanic erruption of humanity let one-third of the island sink into the sea. In 1967 Spiridon Marinatos escavated de remains of a well preserved settlement - Akrotiri - and discover a culture which in technology was centuries ahead of its time.
Sun
26
May
2013
Minoans - Keftiu

The "Minoans" were the first European high culture. The first European throne was found here. They lived among other in a kind of palaces, for example, the palace of Knossos with over 1400 rooms on 3-4 storeys. There was a even a central sewer system, toilets and a type of hot water heating, etc.
Their Scripture - Linear A - has not yet been deciphered. Many well-preserved frescoes have been found that give an insight into the culture. Almost all Images are of women. Women in the role of
priestesses were in the important social functions.
Sat
30
Mar
2013
Çatalhöyük

Approximately 10,000 years ago began a new era for humanity. Agriculture, the domestication of animals and first fired ceramic, etc. allow a new way of life.
Çatalhöyük is an excavation in present day Turkey. It is a settlement from the Neolithic period, located on the plateau of Anatolia and had up to 8000 inhabitants. It was a cultural center. Stone
blades, mirrors and fired ceramics were found there.
It is seem certain now, that women had a central role. Statues represent goddesses, priestesses or queens. Central is a belief about the woman and the bull.
Mon
04
Mar
2013
Venus of Hohle Fels
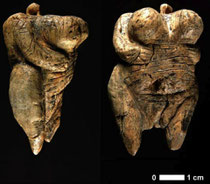
The Venus of Hohle Fels (also known as the Venus of Schelklingen) is an Upper Paleolithic Venus figurine hewn from ivory of a mammoth tusk found in 2008 near Schelklingen, Germany.
It is dated to between 35,000 and 40,000 years ago, belonging to the early Aurignacian, at the very beginning of the Upper Paleolithic, which is associated with the assumed earliest presence of Homo sapiens in Europe (Cro-Magnon).
It is the oldest undisputed example of Upper Paleolithic art and figurative prehistoric art in general.
