Sun
05
Jan
2014
Themistoclea - Teacher of Pythagoras - Priestess of Delphi

Themistoclea was a priestess of Delphi, a well known temple in Greece. She is reputed to have been the teacher of Pythagoras, who is often called "the Father of philosophy".
Sun
05
May
2013
Sappho

Sappho was a Greek lyric poet, born on the island of Lesbos. The Alexandrians included her in the list of nine lyric poets. The bulk of her poetry, which was well-known and greatly admired through much of antiquity, has been lost, but her immense reputation has endured through surviving fragments.
Sappho's poetry centers on passion and love for various people and both sexes. The word lesbian derives from the name of the island of her birth, Lesbos, while her name is also the origin of the word sapphic; neither word was applied to female homosexuality until the 19th century.
An epigram in the Anthologia Palatina ascribed to Plato states:
- Some say the Muses are nine: how careless!
- Look, there's Sappho too, from Lesbos, the tenth.
Sun
21
Apr
2013
Hypatia of Alexandria

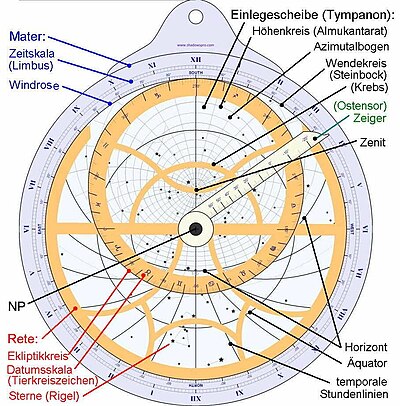
Hypatia was a philosopher and scientist who in the fourth century AD. taught mathematics, astronomy and philosophy at the then famous University of Alexandria, the Museion.
She has invented the astrolabe, with it the position of the stars, the planets and the sun can be determined.
Mon
04
Mar
2013
Agnodice

Agnodice 3rd Century BCE is probably the first physician of antiquity, who has worked as a gynecologist.
Sun
03
Mar
2013
Wencheng - The white Tara

Wencheng has brought Buddhism to Tibet, she is part of the foundation story of Tibet.
Today she is revered as the white Tara, the female Buddha.
Wencheng was the daughter of Emperor Taizong of the Tang Dynasty, she was married as a pledge of peace with Songstan Gampo the first Dharma King of Tibet.
Sun
23
Dec
2012
Cumaean Sibyl

A sibyl is a prophetess, who, unlike other divinely inspired seers foretells the future unsolicited.
It is documented that since 700 BC. there existed Sibyls in Cumae near Naples.
They were the authors of the Sibylline books. These books were used during the Roman Emire by the senate on matters of importance.
